Identity and access management
Identity and access management (IAM) is a set of processes, settings and policies for account identities, authentication and authorization. In simple terms, IAM allows you to organize access to servers.com resources in accordance with your needs in a safe way. The feature is available on the customer portal in the main menu: Identity and Access → Management
The IAM concept is built upon the following terms:
- Resource
- Resource group
- Permission policy
- Team
Each one is considered below in more detail.
Concepts
Resources
A resource is a subject of identity and access management. It can be a server, invoice or Kubernetes cluster. If there are several dedicated servers, each one can be considered as a single resource. A resource may include child entities or specific operations. For example, DedicatedServersOOBAllowPublicAccess - an action to grant public OOB access to a dedicated server.
A resource group is a set of resources grouped by a certain principle.
There are three main resource types. Each resource type is based on its ability to take part in a specific resource group:
- Assignable to resource groups - a resource that is countable and can take part in a group. For example, a dedicated server or a Kubernetes node.
- Aggregative - a resource that contains assignable resources within. Such resources can't be assigned to a resource group (for example, a Kubernetes cluster that consists of Kubernetes nodes).
- Unassignable to resource groups - an unaccountable, abstract resource or something that can't be handled independently (for example, account, invoices or requests).
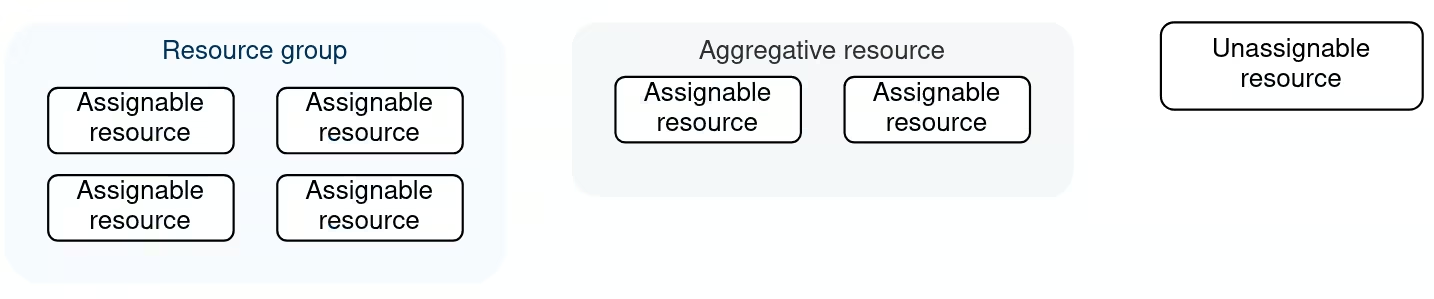
An assignable resource must always be a member of a resource group. Initially, it stays in a default resource group. Adding a resource into a custom group means that it will be removed from the default one.
A resource can be a member of only one resource group.
Permissions
A permission is a right to perform an action on a resource. Here is a list of all main permissions:
- Full access - allow all operations on a resource
- Read - allow visibility over data without the ability to edit a resource
- Management - allow for resource creation, editing, and updating
- Allow delete - allow resources to be deleted
- Allow <action> - allow a specific action
A permission scope is a group of entities united by a certain criteria that can be assigned with permissions. The table below details all permission scopes:
|
Scope |
Description |
Involved entities |
| Administrative | Account management permissions | Accounts, IAM |
| Aggregative | Permissions for aggregative resources | L2 Segments, Firewalls, Kubernetes clusters, Load Balancers |
| Billing | Permissions for finance-related resources | Orders, invoices, account statements, payments |
| Resource-based | Permissions for group-assignable resources (selecting this scope enables the ability to add resource groups) | Dedicated/Cloud/SBM servers, Kubernetes nodes, Cloud Storage, Direct Connect, VPN2GPN, DNS, Private Racks, SSL certificates |
| Support | Permissions for communication with the support team via Requests | Requests |
A permission setting is a list of permissions associated with an entity from a permission scope.
A permission policy is a permission scope with configured settings.
.avif)
Teams
A team is a group of users assigned with permission policies.
.avif)
Use cases
Department-based account access
The most basic scenario for IAM usage is to create a team for each department and assign them with policies related only to their zone of responsibility:
1) Create policies and fill them in with necessary permission scopes:
- "Management policy" with administrative permission scope
- "Financial policy" with billing permission scope
- "Engineering policy" with aggregative, resource-based and support permission scopes
2) Create a team for each department and fill them in with users:
- "Management team" with C-level and team leaders
- "Financial team" with accountants and financial managers
- "Engineering team" with developers, administrators and support
3) Assign policies to corresponding teams:
- Management policy to the management team
- Financial policy to the financial team
- Engineering policy to the engineering team
Servers with restricted access
Sometimes, department-based access is not enough and access to some resources will need to be restricted to just a few employees. Let's say that you have several database servers that only certified employees are allowed to work with. In this case, you'll need to:
1) Create a resource group "DB servers" and add necessary servers there
2) Create a policy "DB certified policy" with the resource-based permission scope and select the "DB servers" resource group
3) Create a team "DB certified team", add users and "DB certified policy"
Getting started
This section will guide you through how to correctly configure identity and access management:
Resource group creation (optional)
This part is optional and is needed only if you want to use the resource-based permission scope. Otherwise, you may skip steps 1-4.
1) Go to the Resource groups tab and create a resource group by clicking the + Create button.
2) Give it a name and description. Click Save.
3) Once a group is created, click it to open its details page.
4) On the details page, click + Add resource button and select necessary resources. Click Save.
Permission policy creation
The steps described below are required and can't be skipped.
5) Go to the Permission policies tab and click + Create button.
6) Give a policy name and description. Select the Permission scope.
Once the resource-based scope is selected, you will be able to add a resource group that you've created in previous steps. In this case, you will see the Select all resource groups and apply to new ones checkbox that will select all existing resource groups and will be applicable to new ones. It means if you add a new resource group later, this policy will be applied to it by default.
Other permission scopes don't operate with resource groups.
7) Depending on a permission scope, you will be offered to select permissions in the Permission settings section for each entity within a scope. Click Add.
Team creation
8) Go to the Teams tab and click + Create button.
9) Give a team name and select Permission policies and Users. Click Save.
Now all necessary entities for proper IAM operation are configured.