4 benefits of virtual private cloud
If you’re looking for public cloud scalability with private cloud security then a VPC could be a great option. Some key benefits of virtual private cloud include:
1. Agility and scalability
VPC solutions usually offer instant scalability allowing you to dynamically scale your resources up and down as needed. A good VPC provider will be able to offer short-term contracts and the flexibility to scale down when demand subsides. Doing this in a virtual environment is typically easier as virtual machines (VMs) are quick to provision and are portable across physical hosts running the same hypervisor.
2. Redundancy/availability
Depending on how your solution is designed, you can plan for fault tolerance within your infrastructure. This means that if a server goes down, your VMs can be easily (often automatically) moved to another physical host. Advanced solutions can even provide disaster recovery across geographically diverse data centers.
3. Enhanced security
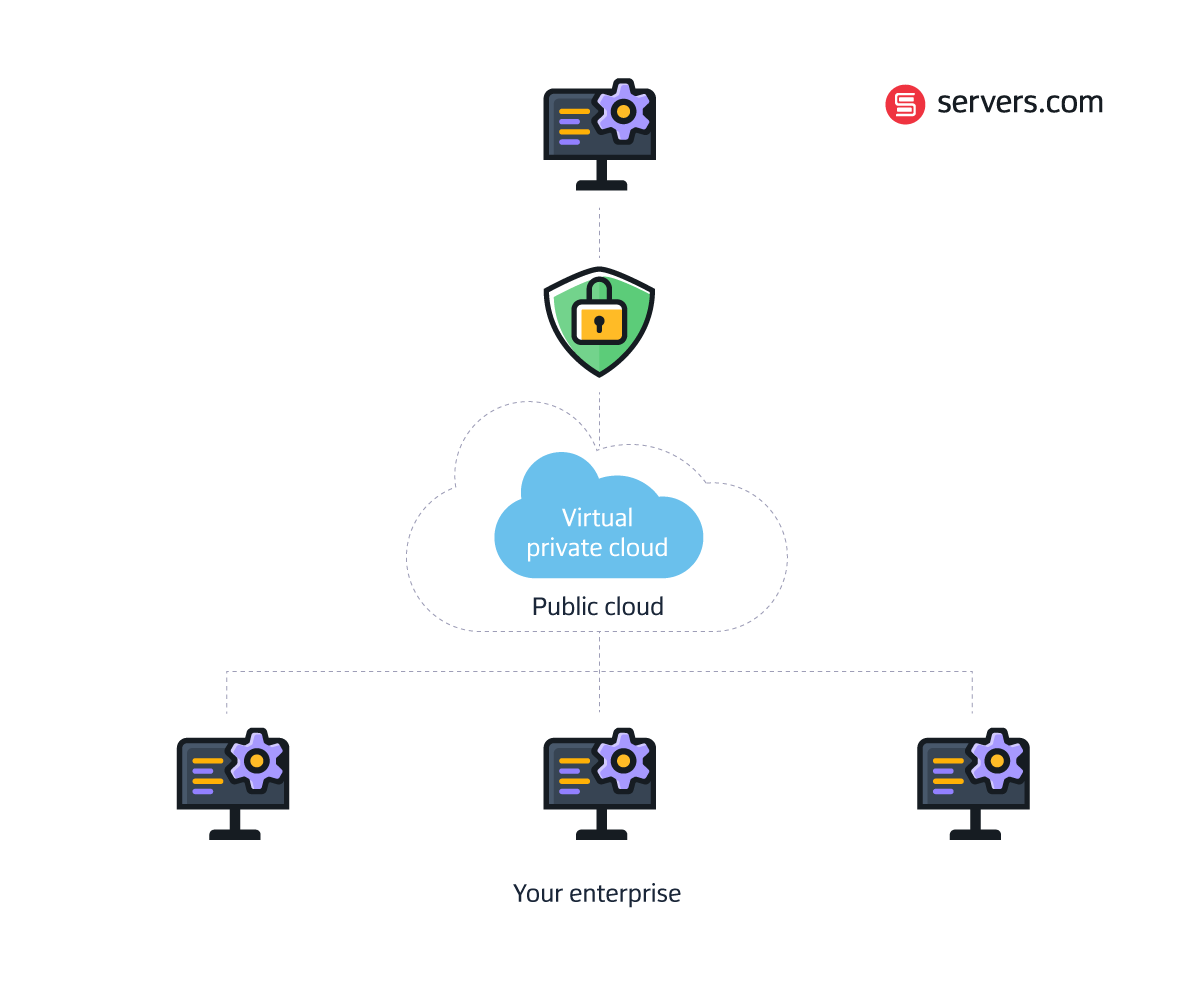
Since a VPC is a logically isolated network, you won’t be sharing compute resources or space with other tenants. VPC is more like a private cloud or a bare metal server in this regard, so you’ll retain control over the security and performance of your data.
4.Lower hardware costs
Depending on your setup, VPCs can be a cost-effective part of your infrastructure, as they typically require less hardware. However, they can be tricky to set up so the cost savings might not be as favourable as public cloud if you’re a smaller business without the expertise required.
Is a VPC right for you? 4 questions to ask yourself
VPCs come with many benefits, but whether a VPC is right for your business depends on what you’re trying to achieve. Questions to ask yourself include:
1. Are your projects underutilizing the full capabilities of your current servers?
If so, then virtual private clouds can give you improved resource utilization and solid availability. By deploying workloads to cloud resources on a needs basis, a virtual private cloud is reactive to the fluctuating demands of growing businesses.
2. Are your requirements large and unpredictable?
VPCs deliver the flexibility of a public cloud, so if your requirements are unpredictable, your VPC server can be adjusted accordingly and sized to meet your changing needs.
3. Is security important to you?
Then virtual private cloud servers win over the public cloud. With a VPC, your data and applications are safe from other tenants. Although the physical infrastructure is shared, thanks to the logically isolated network, your VPC is yours and yours alone.
4. Are you looking for cost-effective hosting?
A VPC may well be the best ‘bang for your buck’. As a multi-tenanted solution, the cost of physical infrastructure is split between all tenants which helps to keep costs down. Plus, you have the flexibility to scale up and down, with short-term contracts allowing you to only pay for what you need.
Ready to set up your new virtual private cloud?
For businesses looking for the scalability of public cloud hosting but with the security of private cloud, VPC solutions offer the happy medium. And because VPCs can be added to hybrid cloud deployments fairly easily, it’s unsurprising that these solutions continue to grow in popularity.




![What is Hybrid Cloud Computing? [Benefits & Limitations]](/dA/6244e47dba/image/Preview.png)

