How to access a Kubernetes cluster
To access and execute commands in a Kubernetes cluster, you can use the kubectl command-line utility. It allows you to deploy applications, manage cluster resources and view event logs.
The utility is cross-platform and can be installed on various operating systems, including Linux, macOS, and Windows.
For more detailed information, including a full list of available commands, refer to the official documentation.
Getting started with kubectl
To avoid unexpected issues, ensure that the kubectl version differs from the cluster version by no more than one minor version.
For example, a client running version v1.31 can interact with control planes running versions v1.30, v1.31, and v1.32.
To check the client version:
-
Go to the customer portal
-
In the left-hand menu, navigate to Kubernetes and select your cluster
-
The cluster version will be displayed in the Version field
Installing kubectl
This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to install kubectl on macOS using curl.
For other operating systems, refer to the official documentation.
Installing the kubectl binary with curl on macOS
-
Download the suitable version by executing the following command in the terminal:
curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/release/{version}/bin/darwin/{CPU}/kubectlReplace:
-
{version}with the required version, e.g.,v1.31.0 -
{CPU}with the correct architecture:-
For Intel: use
amd64 -
For Apple Silicon: use
arm64
-
-
-
Validate the binary file (optional):
-
Download the checksum file:
curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/release/{version}/bin/darwin/{CPU}/kubectl.sha256 -
Validate the binary against the checksum:
echo "$(cat kubectl.sha256) kubectl" | shasum -a 256 --check -
If successful, the output will display:
kubectl: OK -
If the check fails, you will see:
kubectl: FAILED shasum: WARNING: 1 computed checksum did NOT match -
Download the same version of the binary and try again
-
-
Make the
kubectlbinary executable:chmod +x ./kubectl -
Move the
kubectlbinary to a directory included in your system PATH by executing the following commands:sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl sudo chown root: /usr/local/bin/kubectlNote: ensure
/usr/local/binis included in your PATH environment variable. If you receive an error such as No such file or directory, create the directory using the following command:sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/bin -
Verify the installed version:
kubectl version --client
If successful, the output will display the version of the kubectl client.
Configuring KUBECONFIG
To use the kubectl utility with a Kubernetes cluster, you need a configuration file (kubeconfig). This allows you to locate and access one or multiple clusters and seamlessly switch between them. For more details, refer to the official documentation.
-
Download the configuration file for your cluster from the Kubernetes cluster details page in the customer portal:
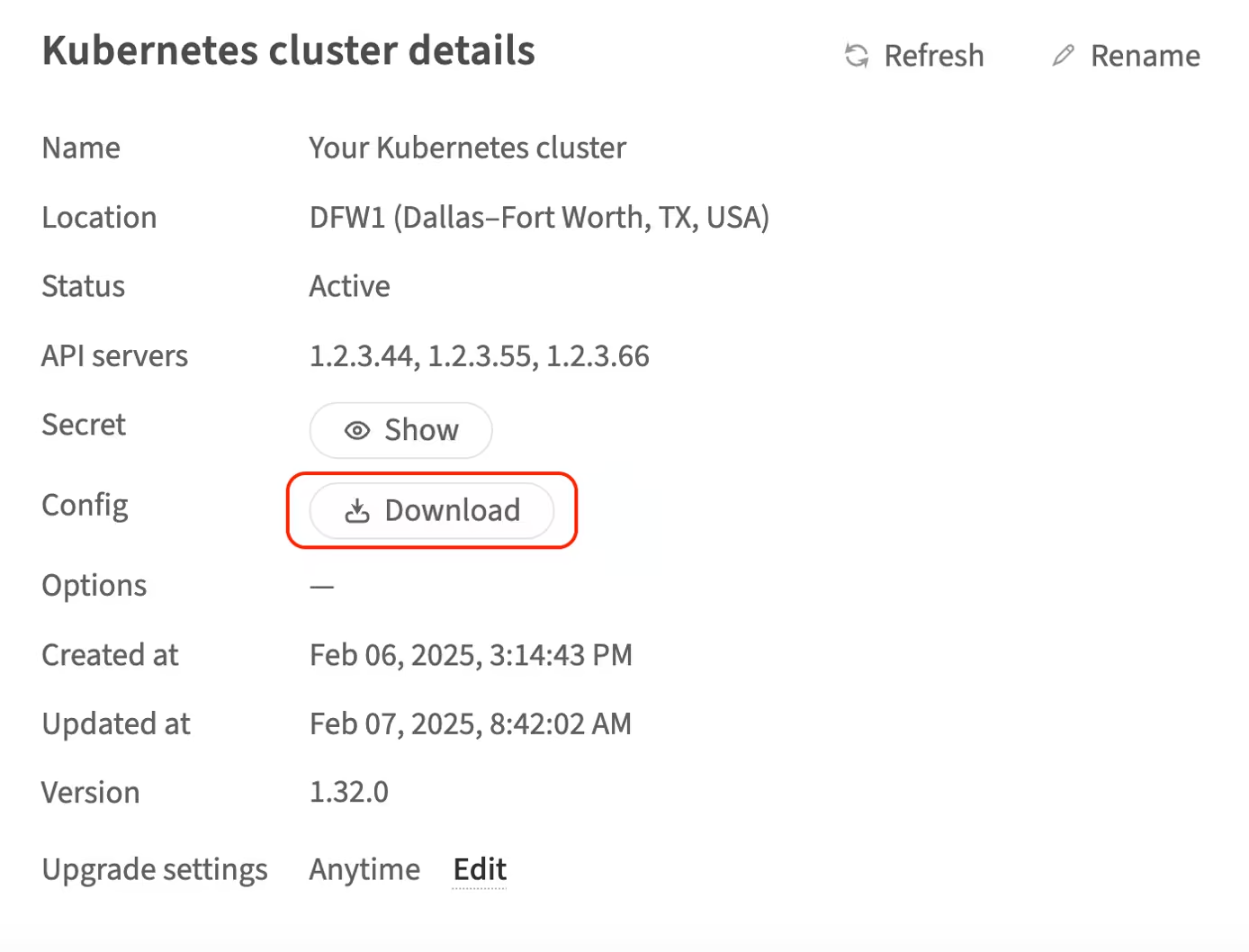
-
Export the KUBECONFIG environment variable, specifying the path to the configuration file:
export KUBECONFIG={path to config file} -
Ensure that
kubectlis properly configured by getting the cluster information:kubectl cluster-info